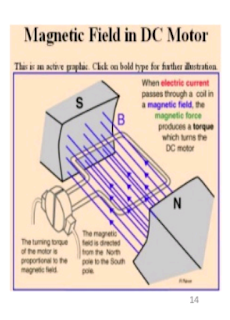
☆ Electrical motor and generator ☆
》 As the electric motor Electromegtets in the spinning stator to turn . There is an electrically slippring on the stator that directs the power to a different magnet section of the stator to achieve rotation Quick
☆Magnetic Storage ☆
》 Magnetic storage ifs magnetic recording are terms from engineering referrinv to the storage of data on a magnetized medium . Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetizing in a magnetizable material to store dtat and is a form of non volatile . The information access using one and more real wire head
☆Magnetic Bearing☆
》A magnetic bearing is a bearing which support a load using magnetic leviation . Magnetic bearing support moving machinery without physical contact for axample they can leviate a rotating shaft and permit leviate motion with very low friction load no mechanical wear .
☆Magnetic Resonance Image MRI☆
》A magnetic resonance algorithm is a type of magnetic resonance imaging scan that uses a magnetic field and pulses of ratio wave energy to provide picture of blood vessels inside the body . In many case MRI can provide information that can not be obtained from a x-rays ultrasound and computed tomography scan.
☆Eddy Current ☆
》 Eddy current brake like a conventional friction brake , is responsible for slowing object, as a train or a roller coaster . However unlike electromechanical brakes, which apply mechanical pressures on two separate objects eddy current brake slow an object by creating eddy current through electromagnetic induction which create resistance and turn it either heat or electricity